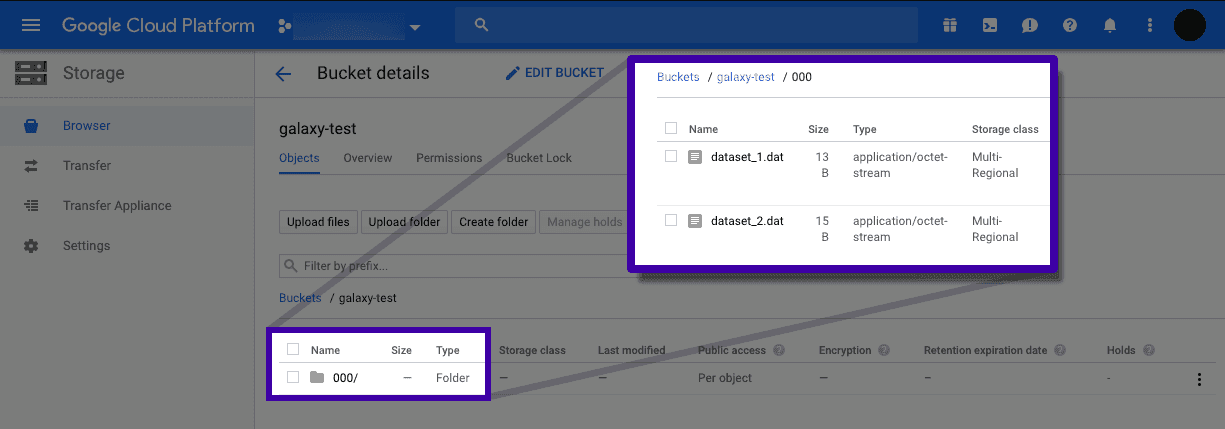
Google Cloud Storage
A Galaxy admin can configure ObjectStore to persist data on a Google Cloud Storage. In the following, first we explain how to setup a bucket on the Google Cloud Storage, and then we discuss how to configure Galaxy ObjectStore to leverage that bucket.
Step 1/2: Configure Google Cloud Storage
In general, to setup Google Cloud Storage, you would first need to create a service accounts from Google Cloud Console and authorize it to read/write storage objects under your account, then obtain the necessary credentials that authorize Galaxy to assume the service account, and finally create a bucket for Galaxy. In order to do so, you may take the following steps:
Create a Service Account
-
Go to console.cloud.google.com and login with your Google credentials. You will then be redirected to your dashboard on Google Cloud Platform:
-
Go to service accounts page as shown in the following figure:
-
Create a service account by clicking on the
CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNTbutton: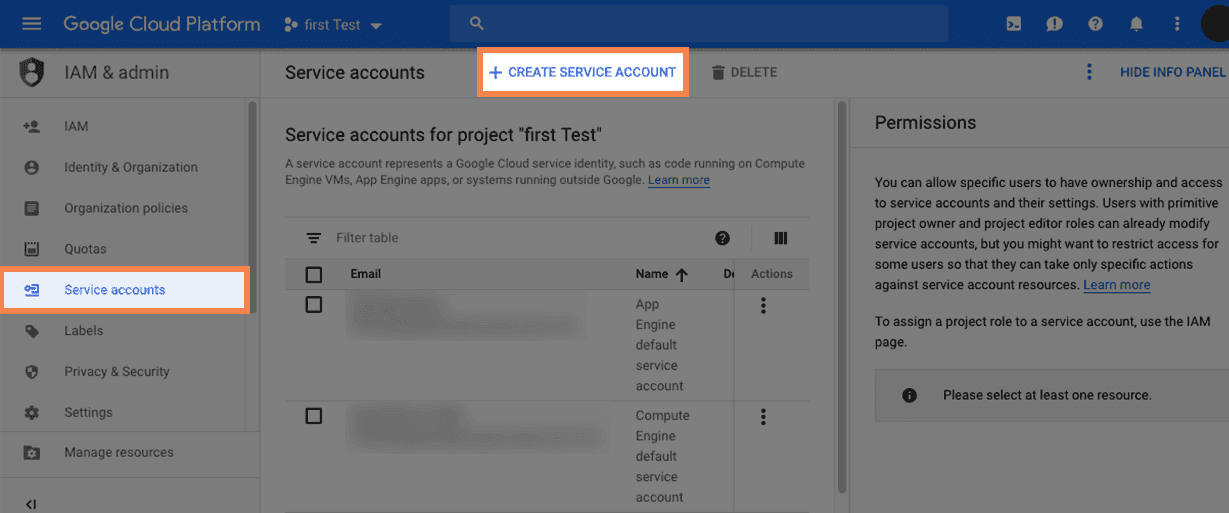
This will create a service account under currently selected project (e.g., the
first Testproject as shown in our example figures). You can select a different project by clicking on the drop-down icon next to the currently selected project and choose a different project from the pop-up window. -
Fill in the required fields for the service account details, then click on the
CREATEbutton.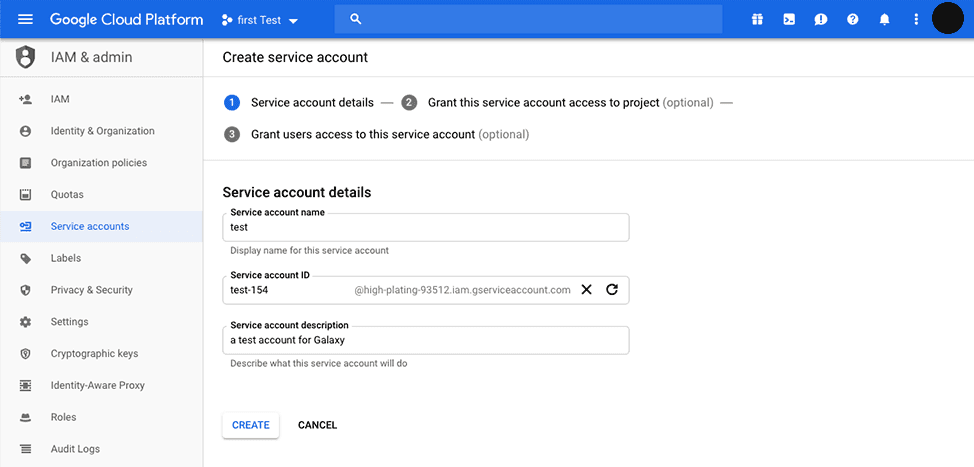
-
Grant the service account with permission to read/write objects in a bucket under your account (e.g., by assigning the
Storage Adminrole to the service account), then click on theCONTINUEbutton. See the following figure: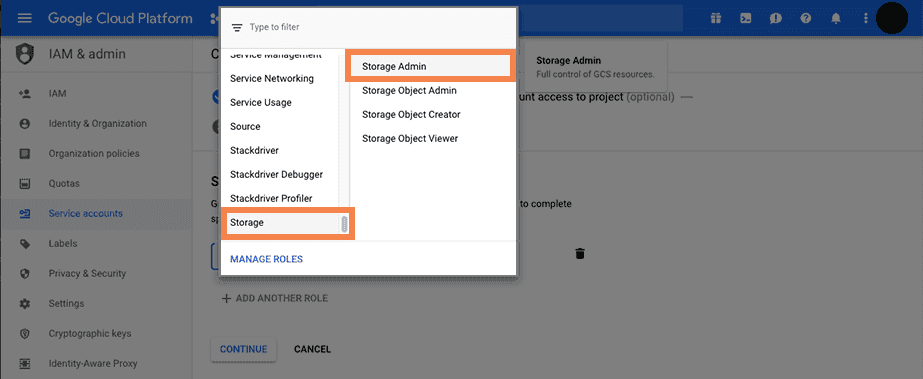
You may refer to the roles documentation page for a complete list of roles and their permissions.
-
On the service account page, click on the
CREATE KEYbutton, then chooseJSON, and then click on theCREATEbutton, and then click on theDONEbutton.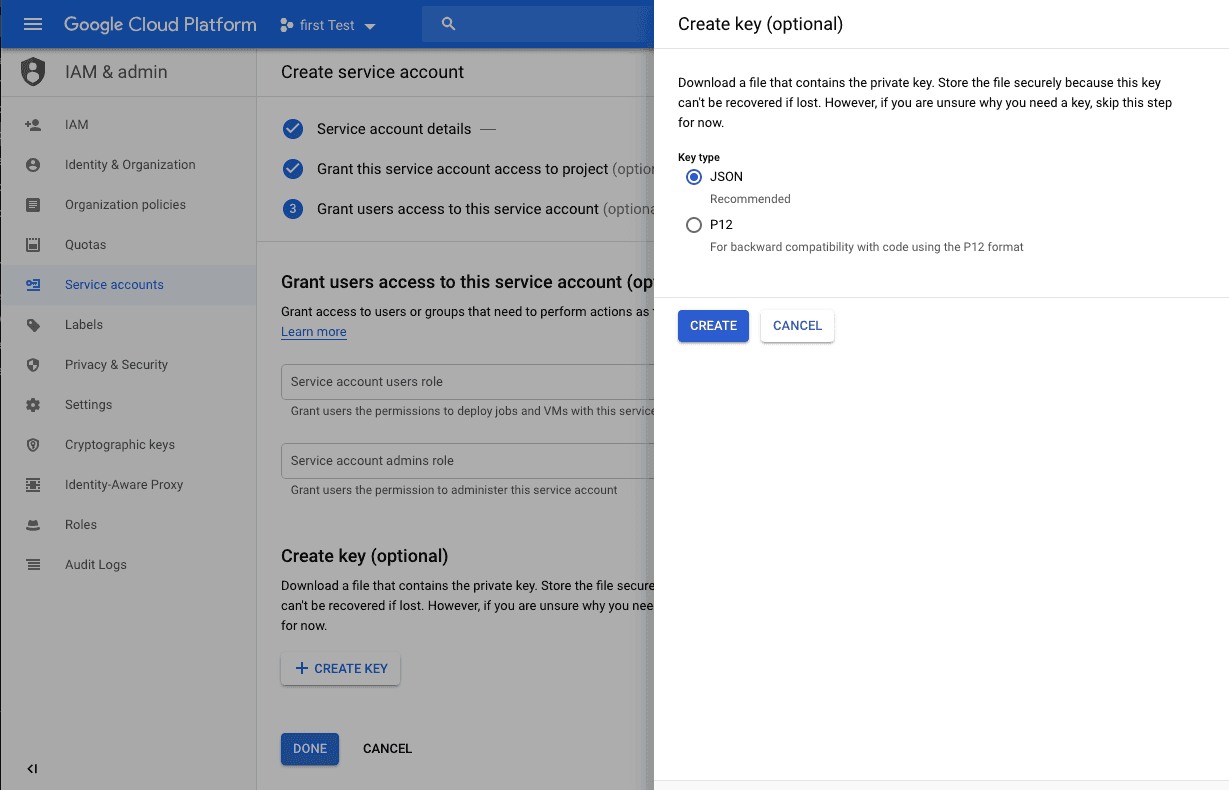
This will create a private key and downloads a json file containing all the required information to access your Google cloud storage under your account.
Create a Bucket for Galaxy
-
On the console page, click on the navigation menu button (
☰), and go toStorage > Browse. See the following figure: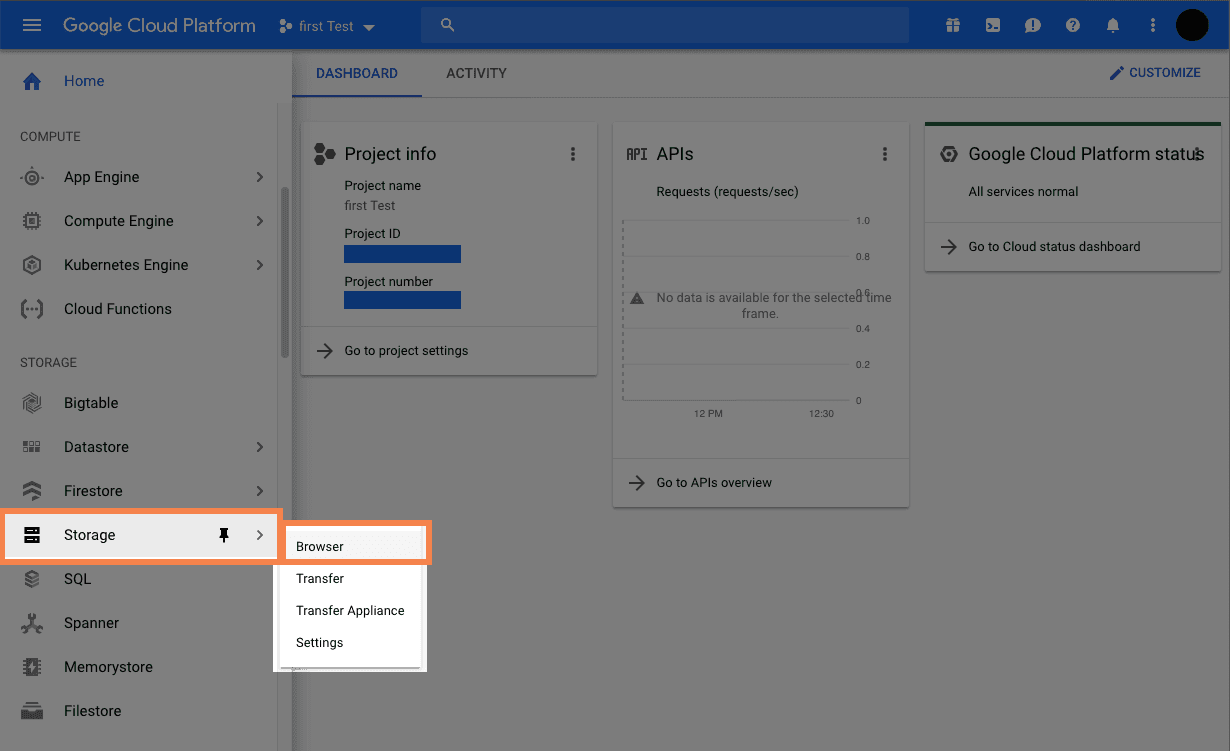
-
On the Storage page, click on the
CREATE BUCKETbutton, see the following figure: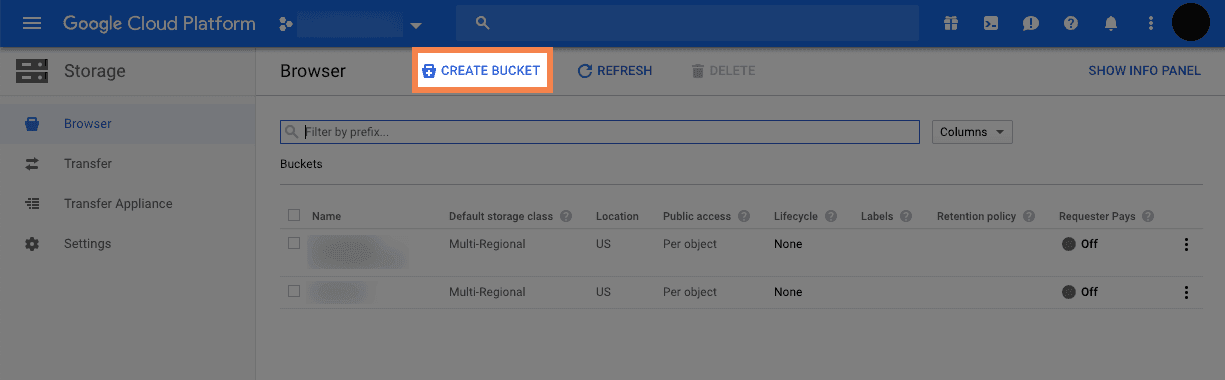
Note: in order to create a bucket, you would need to have an active subscription and have set-up payment options.
-
On the create bucket page, enter the required fields, and note the bucket name, and then click on the
Createbutton.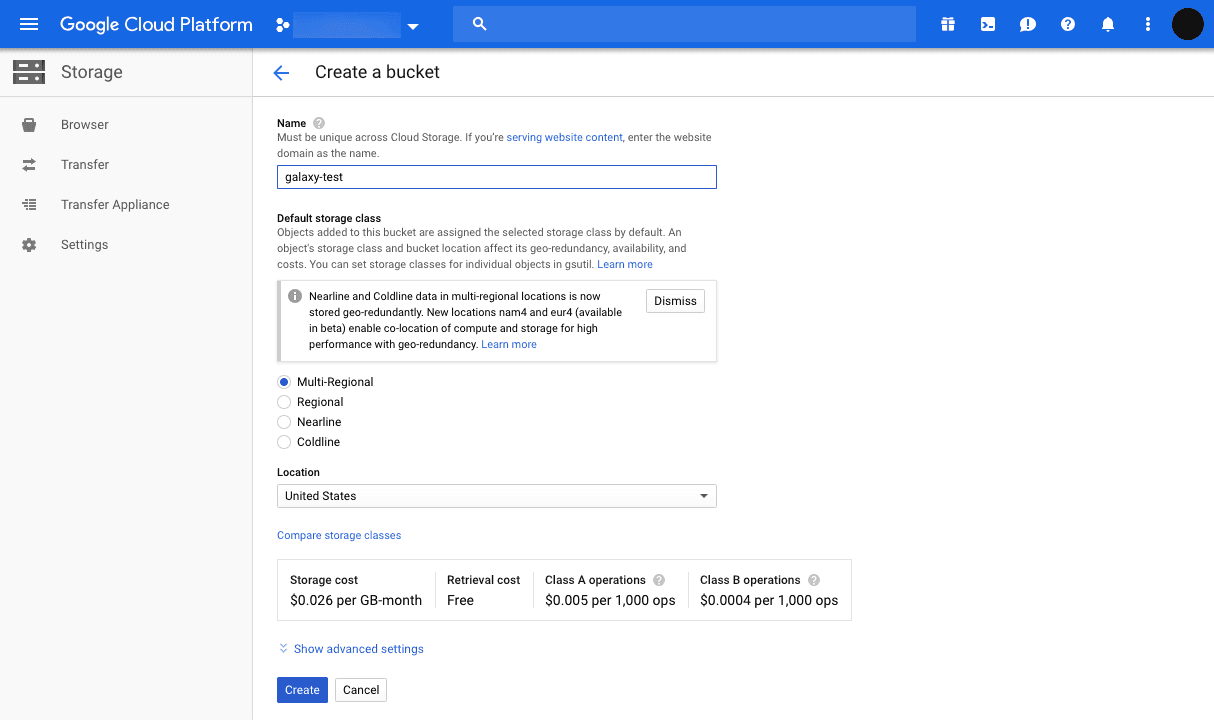
Step 2/2: Configure Galaxy ObjectStore
In order to setup Galaxy to persist data on a Google bucket, you may take the following steps:
-
Enable Galaxy ObjectStore configuration by setting the following key on the
config/galaxy.ymlfile (notconfig/galaxy.yml.sample):object_store_config_file: config/object_store_conf.xml
-
Create the
object_store_conf.xmlfile and set it as the following:<?xml version="1.0"?> <object_store type="cloud" provider="google"> <auth credentials_file="THE_PATH_TO_THE_JSON_FILE_YOU_OBTAINED_FROM_GOOGLE" /> <bucket name="BUCKET_NAME" use_reduced_redundancy="False" /> <cache path="database/object_store_cache" size="1000" /> <extra_dir type="job_work" path="database/job_working_directory_gce"/> <extra_dir type="temp" path="database/tmp_gce"/> </object_store>Note; the above configuration is the minimum set-up required for Galaxy to persist data on a Google bucket; for advanced options (e.g., defining a hierarchy of multiple backends) see Galaxy ObjectStore configuration page.
-
Restart Galaxy for configuration to take place. At this point, any new dataset uploaded to Galaxy, or generated by Galaxy (as a result of tool/workflow execution) will be uploaded to the specified bucket. See the following figure: